Transformations on Exponentials |
|
|
We know that transformations have the ability to move functions by sliding, reflecting, rotating, stretching, and shrinking them. Let's see how these changes will affect the exponential function:
Exponential Function ( y = abx ) Transformation Examples:
Translation y = b(x - h) + k
horizontal by h: vertical by k:
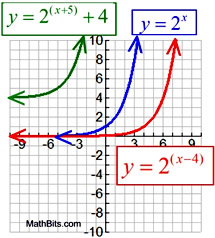
Domain: x ∈ Real numbers
Range: if a > 0, y > k
(if a < 0, range y < k )
|
Translations:
Vertical Shift: f (x) + k
Horizontal Shift: f (x + h)
Reflections:
-f (x) over x-axis
f (-x) over y-axis
|
Reflection
y = a(bx)
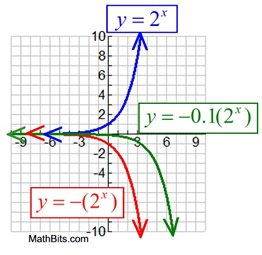
Domain: x ∈ Real numbers
For these examples, if a > 0, y > 0,
if a < 0, y < 0. |
Vertical Stretch/Compress
y = cbx
Stretch (|c| > 1):
Compress or Shrink
(0 < |c| < 1):
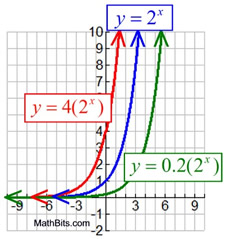
Domain: x ∈ Real numbers
Range: y > 0
|
Vertical Stretch/Compress
c • f (x) stretch ( |c| > 1)
c • f (x) compress (0 < |c| < 1)
Horizontal Stretch/Compress
f (c • x) stretch (0 < |c| < 1)
f (c • x) compress ( |c| > 1) |
Horizontal Stretch/Compress
y = bcx
Stretch (0 < |c| < 1):
Compress or Shrink
( |c| > 1):
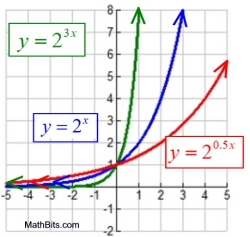
Domain: x ∈ Real numbers
Range: y > 0
|
Overall formula for transformations of an exponential function,
from the parent f(x) = bx, is: y = a • bc(x - h) + k
Note: The independent variable is x with the domain of real numbers.